LeetCode Link: 19. Remove Nth Node From End of List
Problem Definition
Given the head of a linked list, remove the nth node from the end of the list and return its head.
Example 1:
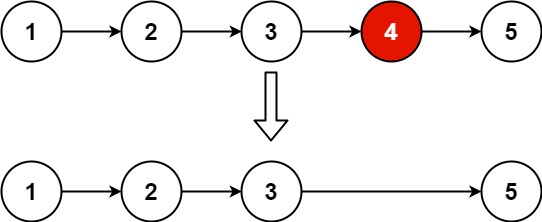
Input: head = [1,2,3,4,5], n = 2
Output: [1,2,3,5]
Example 2:
Input: head = [1], n = 1
Output: []
Example 3:
Input: head = [1,2], n = 1
Output: [1]
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the list is
sz. 1 <= sz <= 300 <= Node.val <= 1001 <= n <= sz
Thought Process
A classic application of the two-pointer technique: to remove the nth node from the end, move fast n steps, then move both fast and slow simultaneously until fast points to the end of the list. You can delete the node pointed to by slow. This is the idea, but pay attention to some details.
The process is as follows (for instance, n=2):
- First, I recommend using a dummy head node here, which makes it easier to handle deleting the actual head node logic. If you're not clear about dummy head nodes, you can refer to this article:

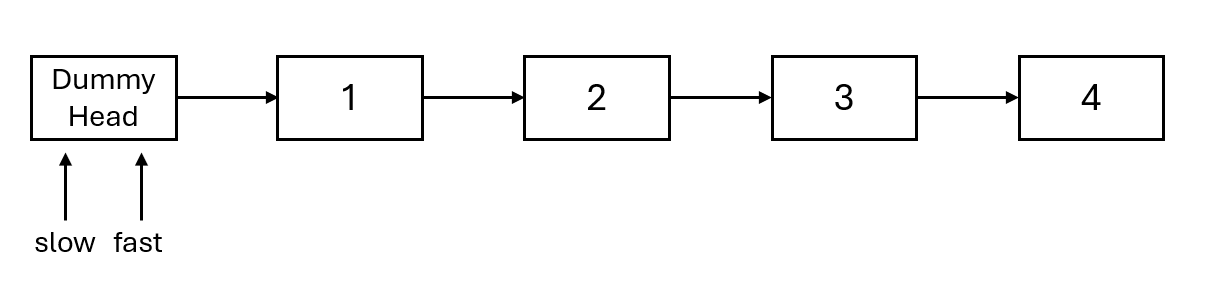
- Define fast and slow pointers with initial values as the dummy head node, as shown in the diagram:
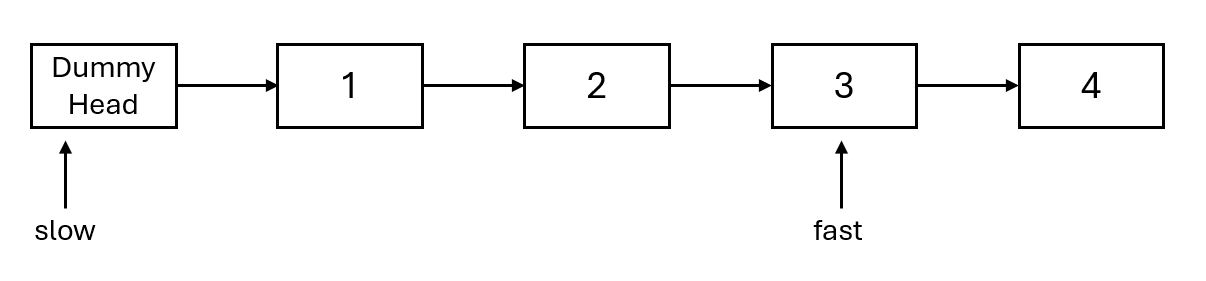
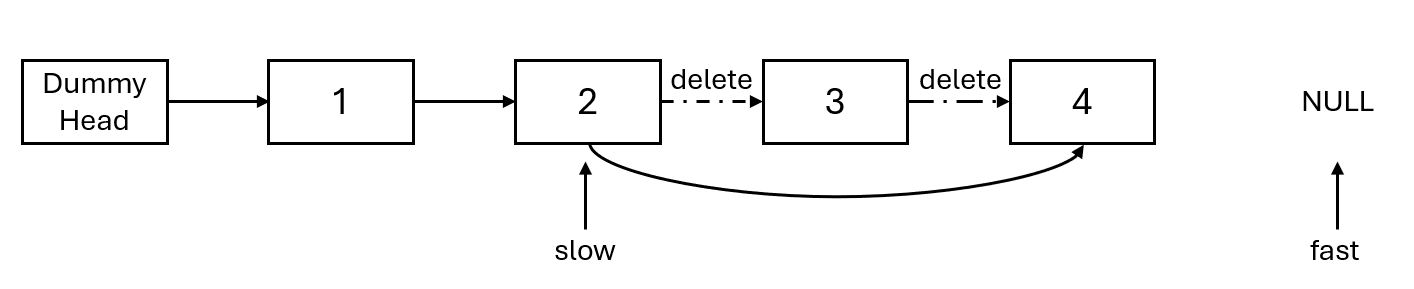
- First, fast takes n + 1 steps. Why is it n + 1? Because only in this way can slow pointer to the node before the one to be deleted when moving simultaneously (making deletion easier), as shown in the figure:
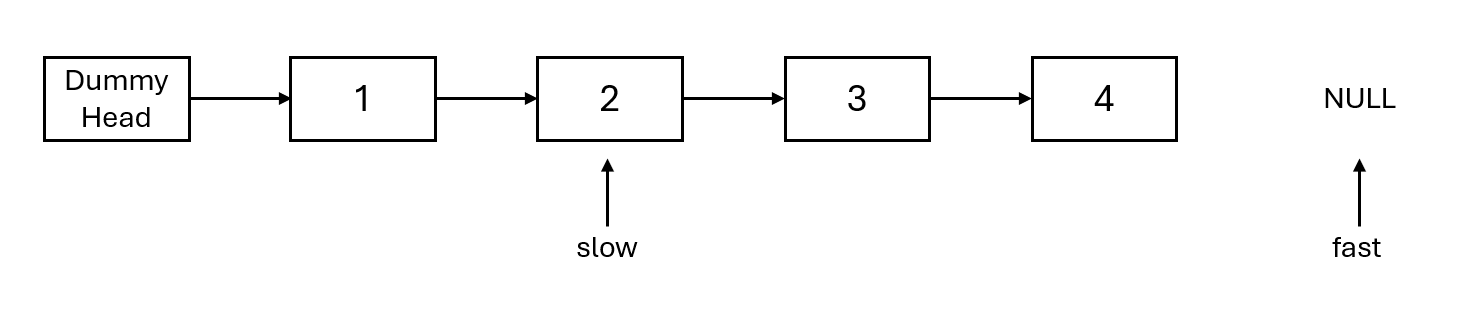
- Fast and slow move simultaneously until fast points to the end, as stated:
- Delete the node pointed to by slow, as shown in the figure:
Solution
# Definition for singly-linked list.
# class ListNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, next=None):
# self.val = val
# self.next = next
class Solution:
def removeNthFromEnd(self, head: ListNode, n: int) -> ListNode:
# Create a dummy node and set its next pointer to the head of the linked list
dummy_node = ListNode(0, head)
# Initialize two pointers, slow_pointer and fast_pointer, both starting at the dummy node
slow_pointer = fast_pointer = dummy_node
# Move fast_pointer n + 1 steps ahead of slow_pointer
for _ in range(n + 1):
fast_pointer = fast_pointer.next
# Move both pointers until fast_pointer reaches the end of the list
while fast_pointer:
slow_pointer = slow_pointer.next
fast_pointer = fast_pointer.next
# Remove the nth node by updating the next pointer of the (n-1)th node
slow_pointer.next = slow_pointer.next.next
return dummy_node.nextTime Complexity: O(n)
Space Complexity: O(1)


Discussion